How can a director and major shareholder limit liability?
Business Law Articles
View more from News & Articles or Primerus Weekly
Russell Advocaten B.V.
Amsterdam, Netherlands
When can a director and major shareholder (DMS) be held personally liable? What can a director and major shareholder do to avoid being held personally liable?
As a director, the director and major shareholder (DMS) may, in certain circumstances, be personally liable for the company's debts. For example, the DMS may be held liable by third parties if he takes too much capital out of the company, so that creditors cannot be paid anymore. The DMS can also be held liable in the event of mismanagement or in the event of a conflict of interest.
The DMS usually has at least two-thirds of equity interest and sufficient voting rights for (almost) full control of the company. He is also the director of the company. This special role may lead to the DMS being more likely to be held liable by creditors. An external financier, for example, could also want the DMS to provide a personal guarantee for the repayment of a loan.
The basic principle is that directors are not liable for debts of the company. This also applies to the DMS. However, in certain cases, directors can be held personally liable by third parties (externally), or by the company itself (internally), or, in the event of bankruptcy, by the trustee in bankruptcy (internally).
Mismanagement
Mismanagement occurs when a director puts at risk the continued existence of the company. The damage can only be successfully recovered from the director if a serious personal reproach can be made against him. Examples of mismanagement are:
Conflict of interest
As a director and shareholder, a DMS wears two hats. As a director, the DMS must focus on the interest of the company. As a shareholder, however, he will also want to receive returns and income from the company. If he pays too much salary or dividend to himself, or borrows money from the company via the current account, he can jeopardise the company’s existence or put creditors at a disadvantage. In this case, there may be personal liability of the DMS.
How can the DMS limit liability?
As a DMS, it is not possible to exclude liability for debts of the company altogether. However, it is possible to significantly limit liability. This can be done by:
Directors’ liability insurance
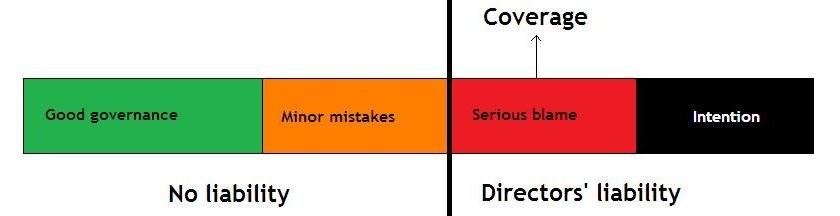
Serious imputable acts can be covered by a directors’ liability insurance (D&O insurance). Damage caused intentionally is not covered.
Discharge from liability
If the shareholders discharge a director from liability, the company and the trustee in bankruptcy can no longer invoke the internal liability of that director. The special feature of the DMS is that he can discharge himself, since the DMS is a director and a major shareholder. Here the risk is that discharge from liability is not formally granted, or that the purpose for which discharge is granted is not laid down. If this is not laid down, it is unclear for what purpose the discharge was granted and the directors’ liability will continue to exist.
Discharge from liability if all shareholders are directors
The following exception to the main rule, that discharge must be explicitly granted by means of a discharging decision, applies. If all shareholders are also directors, the signing of the annual accounts by all directors will be deemed to constitute adoption of the annual accounts. This will automatically result in the directors’ discharge from liability. However, this is subject to the condition that in case there are any other persons entitled to attend the meeting, they have been given the opportunity to take note of the annual accounts and have agreed to this way of adoption. This exception applies to many directors and major shareholders.
Would you like to know more about the liability of the director and major shareholder? Would you like to get advice on limiting your personal liability? Please contact Reinier W.L. Russell (reinier.russell@russell.nl or +31 20 301 55 55).